Knowledge embedded spatial-temporal graph convolutional networks for remaining useful life prediction
Published in Reliability Engineering & System Safety, 2025
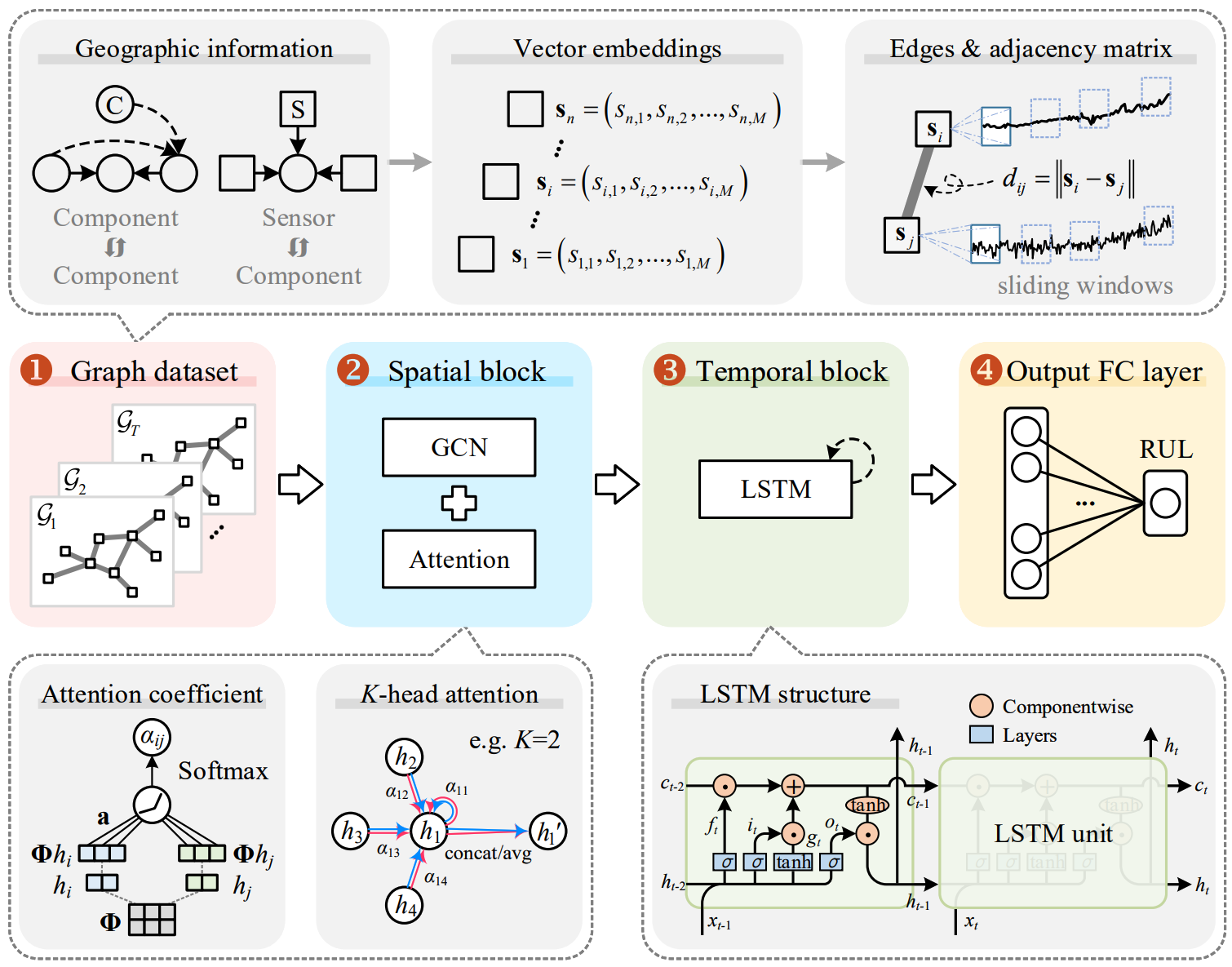
Accurate prediction of remaining useful life (RUL) is crucial for prognostics and health management of equipment. Deep learning methods have gained significant attention in this field, leveraging the abundance of monitoring data captured from sensor networks. However, these methods often overlook the spatial interactions among sensor signals. Moreover, they primarily focus on pattern extraction from sensor data and neglect the utilization of available prior knowledge that could enhance prediction accuracy and stability. To address these limitations, a knowledge-embedded spatial–temporal graph convolutional networks (KEST-GCN) method is proposed. In KEST-GCN, the relationship triplets are established based on the system structure knowledge and sensor position information. Then, these triplets are transformed into low-dimensional vector embeddings using an energy-based knowledge embedded algorithm. After that, the graph dataset is generated, where the embeddings of sensors are utilized to construct the graph edges and weighted adjacency matrix. The weights are dynamically updated by an attention mechanism. Finally, a GCN layer with a multi-head attention mechanism, an LSTM layer and a fully connected layer are employed to extract spatial–temporal degradation patterns and obtain the RUL prediction results. The effectiveness and stability of our proposed method is demonstrated using an aero-engine dataset and a cutting tool dataset, respectively.
Recommended citation: Cai, X., Zhang, D., Yu, Y., & Xie, M. (2025). Knowledge embedded spatial-temporal graph convolutional networks for remaining useful life prediction. Reliability Engineering & System Safety, doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ress.2025.110928.
Download Paper
