A self-data-driven approach for online remaining useful life prediction of machinery using a recursive update strategy
Published in Mechanical Systems and Signal Processing, 2025
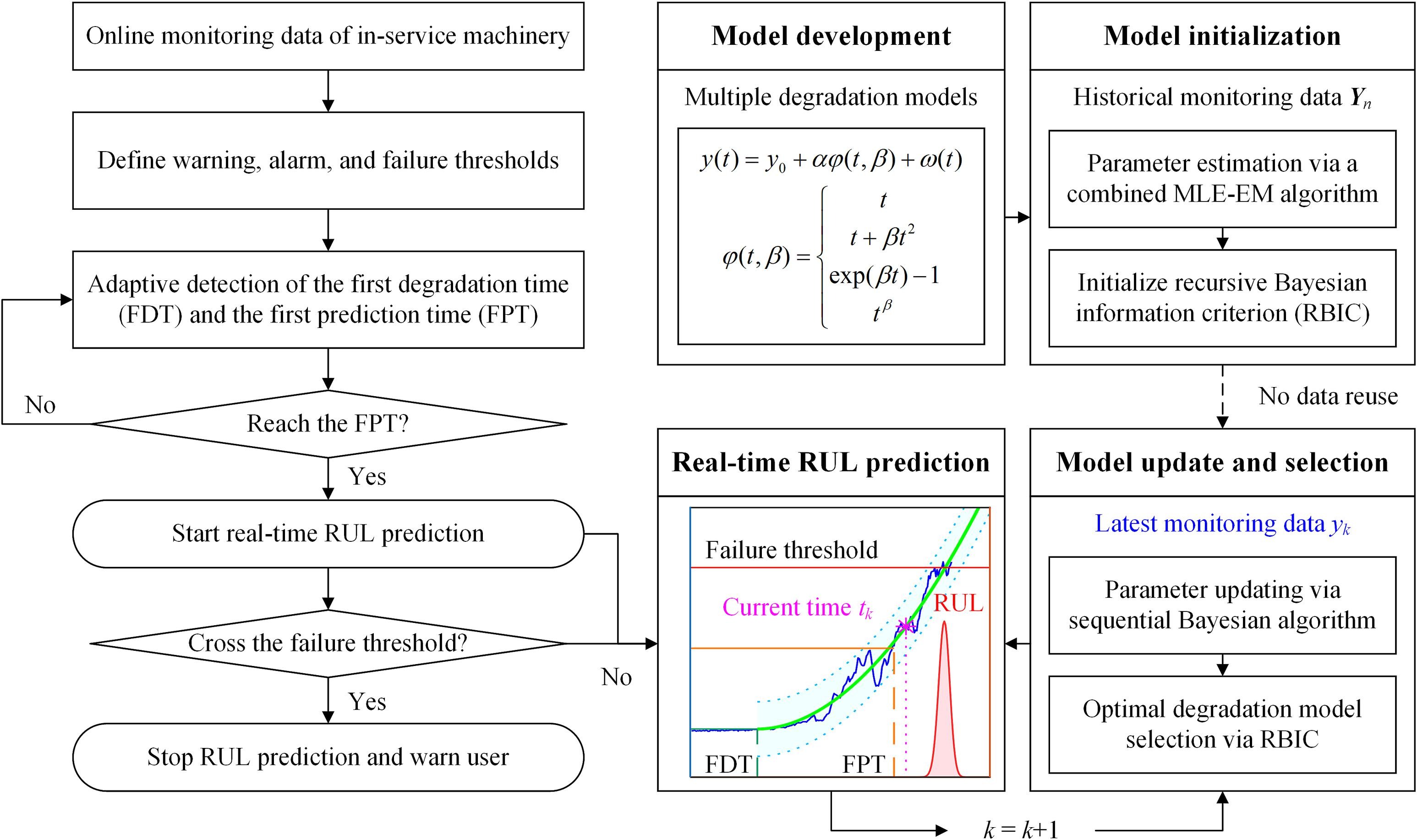
Self-data-driven remaining useful life (RUL) prediction of machinery has gained significant attention in engineering due to its potential to reduce dependency on extensive training data during the prediction process. However, existing self-data-driven methods typically necessitate the storage and reuse of entire historical degradation data for updating prediction models, which limits their applicability in online and real-time scenarios. To overcome this limitation, this paper proposes a self-data-driven method for online RUL prediction using a recursive update strategy. Unlike conventional methods, the proposed recursive update strategy updates model parameters and selects the optimal model based on the latest monitoring data. A model base consisting of various degradation functions is initially established. During online prediction, model parameters are continuously updated in real-time using a sequential Bayesian algorithm, while the optimal degradation model is automatically identified using the proposed recursive Bayesian information criterion (RBIC). The effectiveness of this approach is validated through both simulation and experimental case studies. The results demonstrate that the proposed method not only achieves higher prediction accuracy but also requires less computation time compared to existing methods in online applications.
Recommended citation: Xu, P., Lei, Y., Wang, Z., Li, N., Cai, X., & Feng, K. (2025). A self-data-driven approach for online remaining useful life prediction of machinery using a recursive update strategy. Mechanical Systems and Signal Processing, doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ymssp.2025.112541.
Download Paper
